 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
Disease Name : Lack of Penile Growth
عضو تناسل کی نشوونما کا رکنا |
|
|
|
|
| |

وقت سے عقل کریں |
|
 |
|
| |
Description: Lack of penile growth, Also known as mircopenis.
Organ or part of body involved: Male Sexual Organ
Symptoms and indications: Small penis.
Causes and risk factors: Micropenis can have a variety of causes. Since it is defined statistically, a large proportion of males with micropenis are simply normal but in the lowest percentile of normal size. As for many other conditions, the term "idiopathic" is often used when a cause cannot be determined. Of the abnormal conditions associated with micropenis, most are conditions of reduced prenatal androgen production or effect. Examples include abnormal testicular development (testicular dysgenesis, Klinefelter syndrome, Leydig cell hypoplasia), specific defects of testosterone or dihydrotestosterone synthesis (17,20-lyase deficiency, 5?-reductase deficiency), androgen insensitivity syndromes, inadequate pituitary stimulation (gonadotropin deficiency) or other forms of congenital hypogonadism. Micropenis can also occur as part of many genetic malformation syndromes not involving the sex chromosomes. It sometimes is a sign of congenital growth hormone deficiency or congenital hypopituitarism. Finally, a gene (HOX9) has been identified which affects penis and digit size without detectable hormone abnormalities. Pediatric endocrinologists are usually the physicians to whom these boys are referred. After evaluation to detect any of the conditions described above, micropenis can often be treated in infancy with injections of various hormones, such as human chorionic gonadotropin or testosterone. Most eight to fourteen year old boys referred for micropenis have a penis concealed in suprapubic fat, a large body and frame for which a prepubertal penis simply appears too small, delayed puberty with every reason to expect good future growth. |
Disease Name : Weakness of Male Sexual Organ
|
|
|
|
|
| |

اب پچھتاوے کیا ہووت |
|
 |
|
| |
Description: Weakness of male sexual organ
Persons most commonly affected: Adult Males
Organ or part of body involved: Male Sexual Organ
Prevention: Maintain a healthy diet and watch what is taken into the body. One of the worst things men can do is smoke. Smoking can actually shrink the penis and its effects on health in general are well documented. Excess intake of alcohol can also have a detrimental effect. Apart from impotence, alcohol can also cause a general weight increase. Weight can have a very real effect on the size of the penis as excess body fat can cause more of the penis to remain hidden |
Disease Name : Premature Ejaculation
|
|
|
|
|
| |

ابھی تو آئے تھے |
|
 |
|
| |
Description: Emission of semen prior to or immediately upon engaging in sexual intercourse.
Persons most commonly affected: Adolescents, young adults and other sexually naive males are more likely to experience this condition than other age groups and sexually mature males.
Organ or part of body involved: Male sexual organ
Symptoms and indications: Ejaculation happens before the individual or couple would like. This may range from before penetration to a point too soon after penetration for the couple to feel fully satisfied.
Causes and risk factors: Factors such as lack of sexual experience, lack of knowledge regarding normal male and female sexual responses, and the association of psychological factors (fear, guilt, and anxiety, for example) with sexual activity, all increase risk. The main cause of premature ejaculation is biological. Upon sexual stimulation and arousal, the normal physical responses for a man and a woman are similar. A man will achieve a climax and then ejaculate about two to three minutes after penetrating the vagina. Women will reach orgasm about 12 to 14 minutes after intercourse occurs. Many women do not achieve orgasm especially if only penetration of the vagina by the penis occurs during sexual activity. Many women achieve orgasm through other methods of sexual stimulation although for some, orgasm is not achieved under any circumstances nor with any type of stimulation. Roughly 10% of women fall into this category. Other causes of premature ejaculation include psychological factors such as marital and relationship issues, performance anxiety (with partners new to each other and especially in the inexperienced partner), fear (associated with concerns regarding getting caught or discovered, sexually transmitted diseases or potential pregnancy), and guilt (believing the activity is sinful e.g., premarital or extramarital sex).
Prevention: The knowledge of normal male and female sexual responses prior to engaging in sexual activity may be helpful in preventing premature ejaculation. The emergence of sexual tension and relationship difficulties are greatly reduced if sexual activity occurs under these circumstances: only after the partners know each other well and are comfortable with one another. Both partners consent to sexual intimacy without feeling pressured. Sexual activity should occur in a private and relaxed setting. In addition, contraception issues should be discussed, decided and acted upon by the couple. |
Disease Name : Erectile Dysfunction
|
|
|
|
|
| |

کیا میں مرد نہیں رہا |
|
 |
|
| |
Description: Erectile dysfunction (ED), also known as male impotence, is a sexual dysfunction characterized by the inability to develop or maintain an erection of the penis sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance.
Persons most commonly affected: Most men experience this at some point in their lives, usually by age 40.
Organ or part of body involved: Male sexual organ.
Symptoms and indications: Inability to attain or maintain erection of the penis for sexual intercourse.
Causes and risk factors: Causes are either by physical or psychological problems. It may be brought on by job-related stress, fear of causing pregnancy, unresolved conflicts about sexuality, or fear of sex after a heart attack or major surgery. Drug and alcohol abuse are also among the leading cause of erectile dysfunction. Physical factors include an imbalance in the hormonal system that causes a decrease in production of testosterone (the male hormone necessary for an erection), the use of certain drugs for the treatment of hypertension, particularly diuretics and beta blockers, diseases of the nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis, structural abnormalities of the penis, injury to the penis, and malfunctioning of the circulatory system, which can interfere with the blood flow to the penis, and diabetes. Diet is another common cause. Just as a high-fat, low-fiber routine can inhibit blood flow to the heart, it can also block the arteries that lead to the penis.
Prevention: Limit or avoid the use of alcohol and other similar drugs. Exercise regularly. Reduce stress, get enough sleep, and deal with anxiety or depression. Avoid cigarette smoking and maintain normal blood pressure and cholesterol levels because smoking and high cholesterol can affect blood vessels. Men with diabetes should strive to keep blood sugar levels under control. Because certain medications have been associated with erectile dysfunction, ask your doctor about possible side effects before you start using any new prescription. Eat a healthful diet that is high in biber and nutrients. Good sources of fiber include fresh raw vegetables, apples, oats, and whole grains. Vitamin E dilates blood vessels and improves blood flow. Foods that are high in this nutrient include wheat germ, soy products, leafy green vegetables, and whole grain cereals. Enjoy soybeans, pumpkin seeds, and sunflowe seeds as snacks or in salads. They are excellent sources of zinc, which aids the prostate and improves testosterone levels. Eliminate junk and processed foods from your diet. Do not eat large meals just before sex. Your body will be too focused on digestion to concentrate on desire. Moderate your intake of caffeine and alcohol. |
Disease Name : Sexual Weakness in the Elderly
|
|
|
|
|
| |

مرد اور گھوڑا بوڑھے نہیں ہوتے |
|
 |
|
| |
Description: Sexual weakness in the elderly.
Persons most commonly affected: Males over 50 years of age.
Organ or part of body involved: Male sexual functions
Symptoms and indications: There are several normal changes that occur as a male becomes older. One is a decreased production of testosterone which stabilizes around age 60. The size and firmness of the testicles may be reduced because of this decrease. There is also a reduction in sperm which means a lesser chance of impregnating a female. Another change that occurs is the increase in the size of the prostate (prostatitis) is common and easily treatable with antibiotics and massaging the gland. If there are tumors, surgery may be required. This can cause problems such as a lack of erection because of the absence of hormones from the prostate gland. New surgical procedures can eliminate this threat.
The sexual response cycle also changes as the male becomes older. In the beginning of having sex (excitement phase), the erection may be delayed. Therefore, more direct stimulation of the penis is required. The erection may not be as firm when younger. The male may also experience a longer time before ejaculating (plateau phase) which can be an asset for the female because of the extra stimulation which can help her achieve an orgasm. The orgasm (orgasm phase) for the male is shorter than when younger. The urgency to ejaculate is reduced along with reduction in seminal fluid. The time right after orgasm (resolution phase) when the male returns to the nonexcited phase is of a shorter duration. The time that it takes a male to regroup (refractory period) can take anywhere from 12 to 24 hours or longer before he can achieve another orgasm. This period increases as the male becomes older.
According to some researchers, if a man remains sexually active in his youth and middle years, he can continue to be active in his later life. However, if a man stops having sex in his 50's and 60's, the chance of becoming impotent is greater. If he and his partner are able to use special techniques that rely heavily on genital stimulation, then he will be able to stay sexually active well into his advance years.
Causes and risk factors: The sexual functioning of the elderly can be negatively influenced by drugs prescribed for illness. Many older people (60%) are on drugs for cardiovascular conditions. Forty percent over age 80 are on diuretics which are known to contribute to erectile failure. Thiazides for the control of hypertension in unnecessary high doses also causes problems in erectile functioning.
Many elderly persons (85%) are taking benzodiazepines which can inhibit inhibit intimacy. Alcohol can produce impotency or a lack of sexual desire for both himself and his partner. This is because alcohol depresses the central nervous system which will lead to a reduction in sexual performance. Psychotropic medications may cause temporary impotence. Some other medications that can cause serious difficulties are antidepressants, tricyclics and monamine oxidase inhibitors, and some coronary care medications.
Prevention: In most cases, testosterone therapy clearly improves libido, muscle strength, sense of well-being, and mood. Cognitive performance is highly linked to bioavailable testosterone levels, and testosterone therapy has been shown to improve visual spatial memory in middle-aged men. |
Disease Name : Azoospermia
|
|
|
|
|
| |

سپرم کم یا مردہ |
|
 |
|
| |
Description: Complete absence of spermatozoids in the semen, causing sterility
Persons most commonly affected: Males of fertile age.
Organ or part of body involved: Male reproductive system.
Symptoms and indications: The finding of azoospermia often comes as a surprise since there often are no symptoms (there frequently is an ejaculate and a normal ejaculation process). It is only detectable only by performing a sperm count.
Causes and risk factors: The causes are lack of sperm production due to hormonal problems.
|
Disease Name : Spermatorrhoea
|
|
|
|
|
| |

سپرمز کا بلکل نہ ہونا |
|
 |
|
| |
Description: Abnormal involuntary, too frequent, and excessive discharge of semen without sexual intercourse.
Persons most commonly affected: Adolescent and young adults
Organ or part of body involved: Male reproduction system
Symptoms and indications: General debility, inaptitude to work, disinclination for sexual intercourse and ultimately impotence.
Prevention: Avoid alcohol and caffeine. A low protein diet, free from eggs, may prove beneficial. |
Disease Name : Oligospermia
|
|
|
|
|
| |
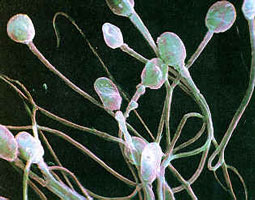
سپرمز کی شدید کمی |
|
 |
|
| |
Description: Abnormally low concentration of spermatozoa in the seminal fluid.
Organ or part of body involved: Male reproductive system.
Symptoms and indications: Seminal fluid where the concentration of sperms is less than 20 million sperms /ml.
Causes and risk factors: Possible causes are constitutional weakness or irregular sexual life, chronic illness including mumps and some sexually transmitted diseases, severe testicular injury, tumour, hormonal deficiencies, varicocele, exposure to toxic chemicals, stress, some antibiotics, alcohol abuse, or weakness or malnourishment of the body.
Prevention: Nutritional and lifestyle changes increase chances for conception. Smoking, caffeine, drug and alcohol consumption, and stress are related to infertility. Reproductive organs are highly susceptible to free radical or oxidative damage from environmental toxicants (pesticides, insecticides, lead, radiation, and heavy metals) and natural aging. Red meat and dairy products contain amino acids which helps in increasing sperm mortality and increasing the number of motile sperms. Oysters, sardines, onions, and cardamom are also helpful. Avoid tight clothing, hot baths and saunas, as overheating the testicles can slow sperm production. |
Disease Name : Night Fall Nocturnal Emission احتلام
|
|
|
|
|
| |

احتلام کا ہونا |
|
 |
|
| |
Description: Involuntary discharge of semen during sleep; also known as nightfall or wet dreams.
Persons most commonly affected: Adolescents and adult men
Organ or part of body involved: Male reproductive system.
Symptoms and indications: May include restlessness, insomnia, mild night sweats, difficult urination, and mild emotional disturbances.
Causes and risk factors: They are more common in males who masturbate less often. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|



